Page 119 - BKT Annual Report 2023 EN
P. 119
ANNUAL REPORT 2023 50
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for the year ended 31 December 2023
(amounts in USD, unless otherwise stated)
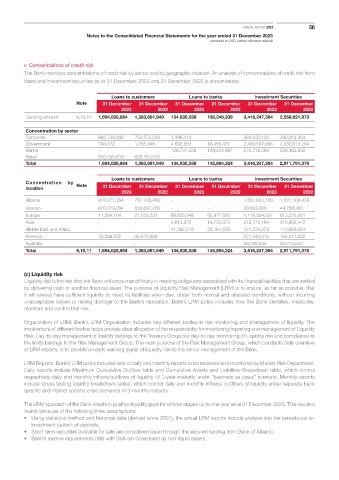
v. Concentrations of credit risk
The Bank monitors concentrations of credit risk by sector and by geographic location. An analysis of concentrations of credit risk from
loans and investment securities as at 31 December 2023 and 31 December 2022 is shown below:
Loans to customers Loans to banks Investment Securities
Note 31 December 31 December 31 December 31 December 31 December 31 December
2023 2022 2023 2022 2023 2022
Carrying amount 9,10,11 1,694,028,984 1,383,681,949 134,830,538 138,246,339 3,416,247,364 2,558,621,973
Concentration by sector
Corporate 882,738,293 753,572,033 3,396,419 - 360,933,122 342,014,464
Government 794,872 1,355,346 4,692,563 16,465,437 2,480,597,956 2,030,613,264
Banks - - 126,741,556 129,428,887 574,716,286 539,163,650
Retail 810,495,819 628,754,570 - - - -
Total 1,694,028,984 1,383,681,949 134,830,538 145,894,324 3,416,247,364 2,911,791,378
Loans to customers Loans to banks Investment Securities
Concentration Note
by location 31 December 31 December 31 December 31 December 31 December 31 December
2023 2022 2023 2022 2023 2022
Albania 978,277,354 767,785,462 - - 1,661,623,750 1,527,106,476
Kosovo 670,879,294 558,697,265 - - 39,803,280 44,769,360
Europe 11,584,104 21,525,333 89,655,048 92,977,620 1,119,504,537 813,078,001
Asia - - 3,613,272 19,755,072 219,772,164 218,982,412
Middle East and Africa - - 41,562,218 33,161,632 124,531,273 113,629,254
America 33,288,232 35,673,889 221,243,815 165,011,032
Australia - - - - 29,768,545 29,214,843
Total 9,10,11 1,694,028,984 1,383,681,949 134,830,538 145,894,324 3,416,247,364 2,911,791,378
(c) Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk is the risk that the Bank will encounter difficulty in meeting obligations associated with its financial liabilities that are settled
by delivering cash or another financial asset. The purpose of Liquidity Risk Management (LRM) is to ensure, as far as possible, that
it will always have sufficient liquidity to meet its liabilities when due, under both normal and stressed conditions, without incurring
unacceptable losses or risking damage to the Bank’s reputation. Bank’s LRM policy includes how the Bank identifies, measures,
monitors and control that risk.
Organization of LRM: Bank’s LRM Organization includes two different bodies in the monitoring and management of liquidity. The
involvement of different bodies helps provide clear allocation of the responsibility for monitoring/reporting and management of Liquidity
Risk. Day-to-day management of liquidity belongs to the Treasury Group but day-to-day monitoring of Liquidity risk and compliance to
the limits belongs to the Risk Management Group. The main purpose of the Risk Management Group, which conducts daily overview
of LRM reports, is to provide an early warning signal of liquidity risk to the senior management of the Bank.
LRM Reports: Bank’s LRM policy includes sets of daily and monthly reports to be reviewed and monitored by Market Risk Department.
Daily reports include Maximum Cumulative Outflow table and Cumulative Assets and Liabilities Breakdown table, which control
respectively daily and monthly inflows/outflows of liquidity till 1-year maturity under “business as usual” scenario. Monthly reports
include stress testing liquidity breakdown tables, which control daily and monthly inflows/ outflows of liquidity under separate bank
specific and market specific crisis scenarios till 3-months maturity.
The LRM approach of the Bank results in positive liquidity gaps for all time stages up to one year as at 31 December 2023. This resulted
mainly because of the following three assumptions:
• Using statistical method and historical data (derived since 2001), the actual LRM reports include analysis into the behavioural re-
investment pattern of deposits;
• Short term securities available for sale are considered liquid through the secured funding from Bank of Albania;
• Bank’s reserve requirements held with BoA are considered as non-liquid assets.